M-WG-AP-Z2-V2
Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car
Soft Tooth Surface
Internal Gear
Cut Gear
Curved Gear
Flexible
Worm And Wormwheel
Moon
Carton
42-Z2
China
Product Description
1, Basic Parameters
-1,Module (m)
Both the axial module of the worm and the end-face module of the worm gear are standard values.
-2,Pressure Angle (α)
The axial pressure angle of the worm is equal to the end-face pressure angle of the worm gear, with a standard value of 20°.-3,Worm Diameter Coefficient (q)
-4,Lead Angle (γ)
Calculation formula: tan γ = z1⋅m/d1, where z1 represents the number of worm threads. -5,Number of Worm Threads (z1) and Number of Worm Gear Teeth (z2)
z1 is typically taken as 1 or 4. z2 is recommended to range from 27 to 80 to strike a balance between structural compactness and transmission smoothness. -6,Addendum Coefficient and Clearance Coefficient
The standard values are respectively 1 and 0.215.2, Transmission Ratio (i)
• Formula: i = z2/z1 (When the worm serves as the driving component).
• Recommended standard transmission ratios: 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80.
3,Geometric Dimension Calculation
Pitch Circle Diameter o For the worm: d1 = q⋅m; for the worm gear: d2 = m⋅z2.
-1,Center Distance (a) o Formula: a = (d1 + d2 + 2x2m)/2, where x2 is the modification coefficient of the worm gear.
-2,Lead of the Worm (S) o S = π⋅m⋅z1.
-3,Diameter of the Worm Gear Addendum Circle o da2 = (z2 + 2)⋅m.
4, Meshing Conditions
-1,Correct Meshing Conditions o The axial tooth pitch of the worm is equal to the tooth pitch of the worm gear's pitch circle. o When the crossed angle is 90°, the lead angle of the worm is equal to the helix angle of the worm gear and they have the same direction of rotation.
-2,Standardization Requirements o To ensure meshing accuracy, processing should be carried out using a worm gear hob that matches the parameters of the worm.
5, Precautions for Parameter Selection
- Number of Worm Threads and Transmission Efficiency o A small number of threads (such as a single thread) can achieve a large transmission ratio and self-locking, but the efficiency is low; a larger number of threads leads to higher efficiency but greater processing difficulty.
- Limitations on the Number of Worm Gear Teeth o Avoid too few teeth causing undercutting or too many teeth resulting in insufficient stiffness.
- Lead Angle and Self-locking o Self-locking can be achieved when the lead angle is less than 3.5°.







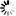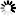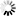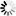
 Audited Supplier
Audited Supplier










