
Timing belts, also known as cam belts, are typically installed on the rotating mechanism of the power transmission system.
Their common role is that they play a vital role in the smooth operation of the internal combustion engine.
They connect the crankshaft with the camshaft to maintain precise alignment (timing) between these two critical components as they rotate at different speeds, but the relative speed is consistent.
Construction:Rear Rubber,Tension Member,Teeth Rubber,Bottom Fabric
Functions:, Protect Tension Member
The Primary Material For Transferring Power
Protect Tension Members & Maintain Belt Shape
Maintain Belt And Teeth Shape
HNBR: Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber CR: Chloroprene Rubber



| Construction | Functions | Materials |
| Rear Rubber | Protect Tension Member | CR, HNBR |
| Tension Member | The Primary Material For Transferring Power | Glass Fiber |
| Teeth Rubber | Protect Tension Members & Maintain Belt Shape | CR, HNBR |
| Bottom Fabric | Maintain Belt And Teeth Shape | Nylon |

- Solves potential problems caused by conventional metal
chain.
- Easily designed to span the distance between drive
pulley sand main retains constant tension.


- Prevents belt elasticity by using glass fibers for the
tension member
- Guarantees high-power transmission efficiency under
driving conditions of high speed and severe temperature
fluctuation


- Excellent in resistance against heat, oil, and wear.
- Stable performance at high-speed rotation







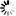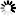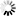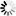
 Audited Supplier
Audited Supplier










