DN15-DN300
ANSI, DIN, GB, JIS, GOST, BSW
Threaded Connection Flange
Carbon Steel
Lateral
Screws
FF
Forging
Carbon Steel
Weight
Strength
Sealing Surface Forms
Plastic
Gaskets
Good Sealing Performance
Sealing Function
Shock Absorption and Buffering
Corrosion Resistance and Oxidation Resistance
Prevent Leakage Problems Caused by Deformation.
SHANXI JINYU
Plywood Case
DN15-DN300
China Shanxi
73079100
Product Description



Structural characteristics
Connection method: The inner hole of the flange is processed into pipe threads, and it is screwed together with a pipe with external threads for matching to achieve the connection. It belongs to a non-welded flange.
Sealing surface forms: Commonly seen ones include raised face (RF), flat face (FF), male and female face (MFM), female face (FM), male face (M), tongue and groove face (TG).
Sealing surface forms: Commonly seen ones include raised face (RF), flat face (FF), male and female face (MFM), female face (FM), male face (M), tongue and groove face (TG).

Performance characteristics
Convenient installation: There is no need for welding. The connection between the pipeline and the flange can be completed through the screwing of threads. It has obvious advantages in some occasions where welding is not allowed on site, such as flammable and explosive areas, places with fire prevention requirements, etc. The installation and disassembly are fast, which can save a lot of construction time and labor costs.Easy maintenance: When the pipeline system needs maintenance or component replacement, the threaded flange can be easily unscrewed to inspect or replace the relevant components without damaging the welded joints or performing complex cutting and welding operations.
Strength adaptation: Threaded flanges made of alloy steel have high strength. For some alloy steel pipelines that are difficult to weld or have poor welding performance, choosing threaded flanges can ensure the connection strength while avoiding problems caused by welding.
Limited application scope: Under the conditions of rapid temperature changes in the pipeline or when the temperature is higher than 260°C or lower than -45°C, the geometric shape of the threads may be deformed, resulting in an increased risk of leakage, and it is not recommended to use them. It is also not suitable for working conditions where crevice corrosion, extreme erosion, or cyclic loading may occur.
Application scope
Utility field: It is often used in pipeline systems for utility services such as instrument air, plant air, nitrogen, drinking water, and raw water. The pressure class generally does not exceed Class 300.Small pipeline systems: Due to its structural characteristics and size limitations, it is usually used in small pipeline systems with a diameter between 1/2 inch and 4 inches, and those within the range of 1/2 inch to 2 inches are more common.
Pipelines of specific materials: It is often used in conjunction with cast iron and galvanized pipelines, such as the tap water pipelines for home entrances.







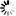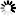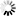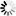
 Audited Supplier
Audited Supplier









